
EPS excluding extraordinary items: This EPS calculation excludes items that are not ordinary in a company's operations, such as the recorded gain or loss on the sale of a large asset, which could skew the results of a EPS calculation.EPS from continuing operations: This only includes EPS from day-to-day operations and does not include discontinued operations, extraordinary items or accounting changes.Diluted EPS: This EPS calculation takes into account a company's convertible securities.EPS: This is the standard EPS calculation, which is net income minus preferred dividends, divided by common shares outstanding.The 4 types of earnings per share metrics are: But there are other types of earnings per share, the main ones being diluted EPS, EPS from continuing operations, and EPS excluding extraordinary items. The standard earnings per share calculation is often referred to as basic EPS. EPS is also used in other valuation metrics, such as the Price-to-Earnings ((P/E)) ratio, which is a company's share price divided by its earnings per share, and the Price/Earnings-to-Growth ( PEG) ratio, which is the company's P/E divided by its growth rate over a certain period of time.

What Is EPS Used For?ĮPS can be used for more than just finding the profitability of a company on a per-share basis.
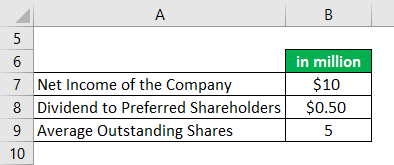
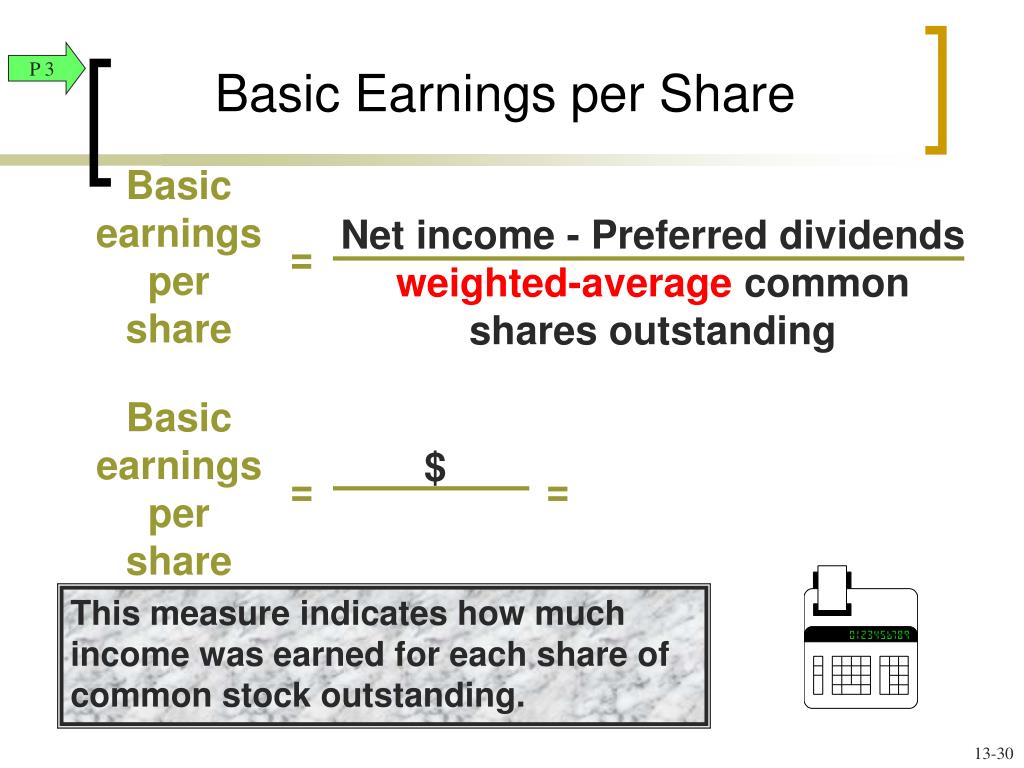
Then you can divide this number by the number of shares of stock it has outstanding. If there are any preferred dividends, subtract them from the annual net income. Publicly traded companies are required to file quarterly Form 10-Q and an annual Form 10-K with the Securities Exchange Commission, or SEC. Tip: To find the numbers you need to calculate EPS for yourself, you can look at a company's public filings. XYZ company had 50,000 shares of common stock outstanding during the year. To calculate EPS, you'll first subtract any preferred dividends from the company's net income, then divide by the number of share of common stock outstanding.ĮPS = (Net Income - Preferred Dividends) / Common Shares Outstandingįor a simple example of calculating EPS, let's say XYZ Company has net income during the year of $1,000,000 and there are no preferred shares outstanding. So, EPS can be described as the amount of money each share of stock would receive if a company's profit was distributed to shareholders at the end of the year. In simple terms, EPS is a calculation that shows how profitable a company is, per share. Because it's a measure of profitability on a per-share basis, EPS is commonly used by investors to estimate the value of a company, per share. It is a tool that Market participants use frequently to gauge the profitability of a company before buying its shares.Stanciuc/iStock via Getty Images What Is EPS? Earnings Per Share DefinedĮPS, which stands for earnings per share, represents a company's annualized net profit divided by the number of common shares of stock it has outstanding. It is calculated by dividing the company’s net Income with its total number of outstanding shares. EPS is a financial ratio, which divides net earnings available to common shareholders by the total outstanding shares over a certain period of time.Įarnings per share or EPS is an important financial measure, which indicates the profitability of a company. It is common for a company to report EPS that are adjusted for extraordinary items, potential share dilution. EPS serves as an indicator of a company's profitability. Earnings Per Share - EPS Updated on J, 9611 views What is Earnings Per Share - EPS?Įarnings per share (EPS) is the portion of a company's profit allocated to each share of common stock.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
